Want a 10% discount on your first purchase?
Sign up for our newsletter
theme575
You have no wish lists..
Your shopping cart is empty!
Once you’ve selected your products,
click the Add to Cart button
Folic acid is a vitamin used to prevent anemia and other disorders of the hematopoietic system. The active component belongs to the bio-substances of the B group. It is water-soluble.
Read more...The main task of the component will be to adjust the harmonious synthesis of nucleic and amino acids, to regulate the production of white blood cells.
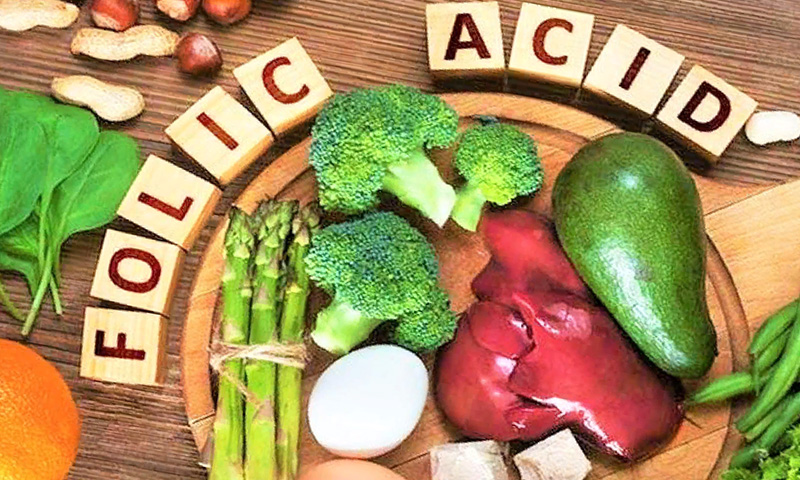

The active component enters the body during a meal. The synthesis of intestinal microflora breaks down and absorbs useful compounds. The main natural "suppliers" include greens and vegetables, nuts, tropical and local fruits, legumes, fish (salmon, tuna, chum salmon), dairy products, and egg yolk.
Folic acid is an essential element of the cellular structure. Its deficiency causes disorders in hematopoiesis, the formation of new red blood cells. The mood deteriorates noticeably, the immune system drops, and there are problems in the gastrointestinal tract.
The effect of the supplement on the body:
B9 Folic Acid is an excellent supplement for the treatment of cardiovascular and immune system problems.
Detailed information on the acceptable amount of the additive is provided in the chart:
|
Age/gender |
The daily value (mcg) |
|
Babies |
40 |
|
6-12 months |
60 |
|
1-3 years |
70 |
|
4-6 years old |
100 |
|
7-10 years |
150 |
|
Teenagers of 11-14 years old |
200 |
|
Pregnant/lactating women |
600/500 |
|
Adults |
400 |
With a deficiency of this element, almost all body systems are damaged. Folic hypovitaminosis manifests itself through:
Both the lack and the excess of the active substance have a negative effect on the body. Oversaturation of the blood with folic acid causes hyperexcitability, dyslexia.
The regulation of all elements requires careful calculation of the course of intake. For example, with the constant addition of B12, B6, the amount of B9 sharply decreases. On the contrary, several courses of folic acid will reduce the amount of B12. Also, corticosteroid hormones and aspirin-based drugs stimulate the withdrawal of the element from the body.
Additional vitamin C will help to quickly assimilate the substance. It is important to consider the general state of health since, for some diseases, the intake of folic acid is prohibited.
Folic acid is actively involved in the creation of red blood cells. Lack of vitamin B9 is accompanied by drowsiness, lethargy, dizziness, decreased immunity.
When there is a lack of folic acid in the body of a pregnant woman, it is accompanied by constant mood swings, confusion. The skin becomes pale and covered with acne. In addition, it is the only prevention of congenital defects of the fetal neural tube
Folic acid was first synthesized from spinach. Later, it was found in boiled legumes, pork liver, asparagus, offal, whole wheat, linseed oil. The human body is not able to independently produce vitamin B9.
There are no products to list in this category.
Want a 10% discount on your first purchase?
Sign up for our newsletter
Want a 10% discount on your first purchase?
Sign up for our newsletter